EPI-MODELS
Stochastic Spread Epidemiological Models: Simulating pest and disease dynamics
Simulation modeling provides a comprehensive analysis of population and transmission dynamics, epidemic scenarios,
and quantitative investigations of intervention efficacy at multiple scales.
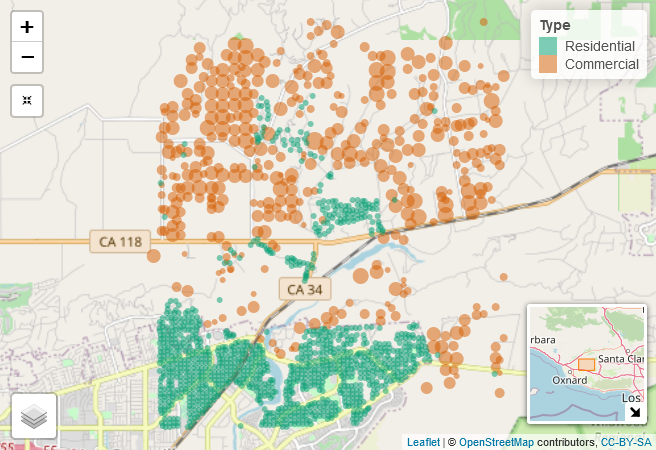
Agent-Based Model
A highly flexible and dynamic spatially-explicit model that simulates the spread of ACP and HLB
in large-scale landscapes.
This provides the opportunity to run scenario-based simulations to evaluate the efficiency and
sustainability of all types of fixed as well as reactive management programs.
Contact modeling team to request access to online interface.
HLB
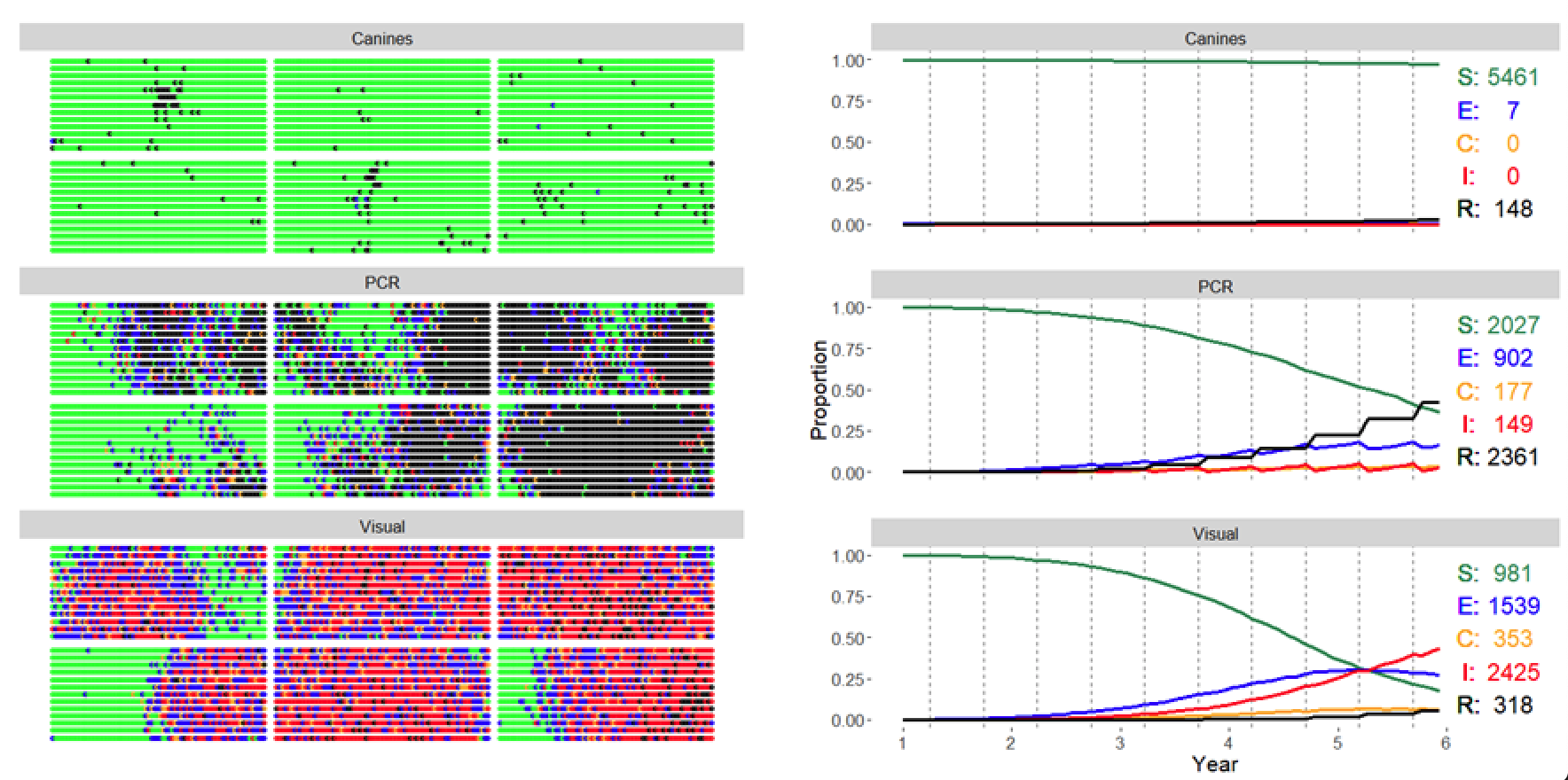
Epidemiological Simulation Model
An individual-based epidemiological model to analyze cost-effective mitigation practices at the farm-level.
In particular, as early detection techniques (EDTs) progress and develop, economic sustainability of the detection technology implementation
and the detection efficiency are both of critical importance.
Read more…
Gottwald T, Poole G, McCollum T, Hall D, Hartung J, Bai J, Luo W, Posny D, Duan Y-P, Taylor E, da Graca J, Polek M,
Louws F, and Schneider W. Canine olfactory detection of a vectored phytobacterial pathogen, Liberibacter asiaticus,
and integration with disease control. PNAS 117:3492-3501
https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1914296117
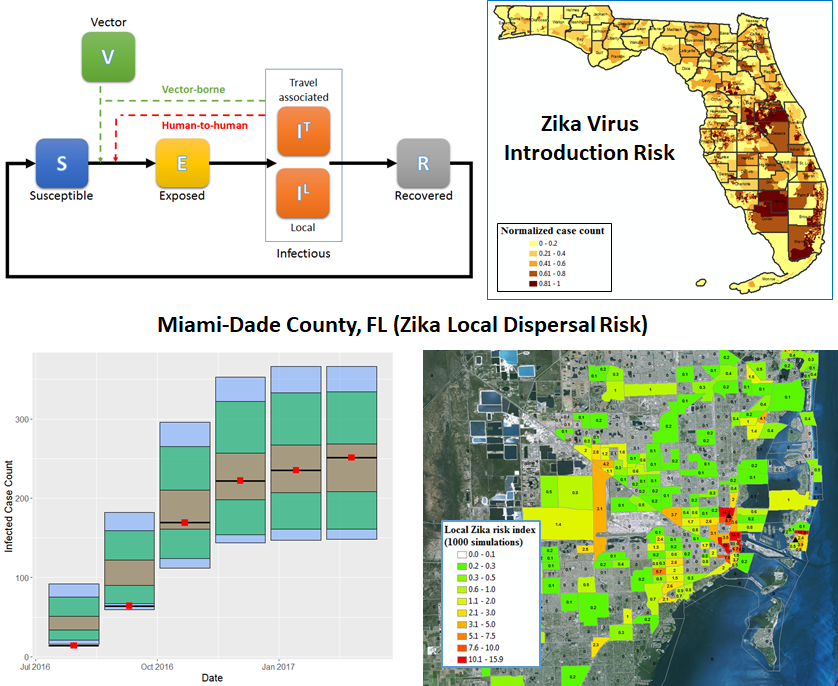
The potential for rapid dispersal of diseases due to the extensive breadth of global travel emphasizes the critical need for early
detection and prompt surveillance of introductions to guide timely mitigation efforts of regulatory agencies, particularly in areas at
high-risk for further local spread (e.g. Covid-19 pandemic and recent Zika outbreaks throughout the Americas).
Human Mobility Model
A spatially-explicit, stochastic Susceptible-Exposed-Infectious-Recovered (SEIR)
framework incorporating introductions by travelers (Introduction Risk Model), seasonal influence on local disease spread
(e.g. climate-driven heterogeneous vector distributions), and propagation through anisotropic human mobility patterns.
An interactive interface is under development.
Covid-19
Zika